Island nations call for oil tax, anti-fossil fuel treaty at UN summit

Small island nations led calls at the UN climate summit Tuesday to tax oil companies' windfall profits to pay for damages caused by natural disasters and enact a "non-proliferation treaty" to halt fossil fuel production.
Developing nations have pressed their case at the COP27 summit in Egypt for the creation of a "loss and damage" fund, arguing that rich nations are to blame for the biggest share of greenhouse gas emissions.
Oil companies have scored tens of billions of dollars in profits this year as crude prices have soared in the wake of Russia's invasion of Ukraine.
"It is about time that these companies are made to pay a global COP carbon tax on these profits as a source of funding for loss and damage," the prime minister of Antigua and Barbuda, Gaston Browne, told fellow leaders at the summit in the seaside resort of Sharm el-Sheikh.
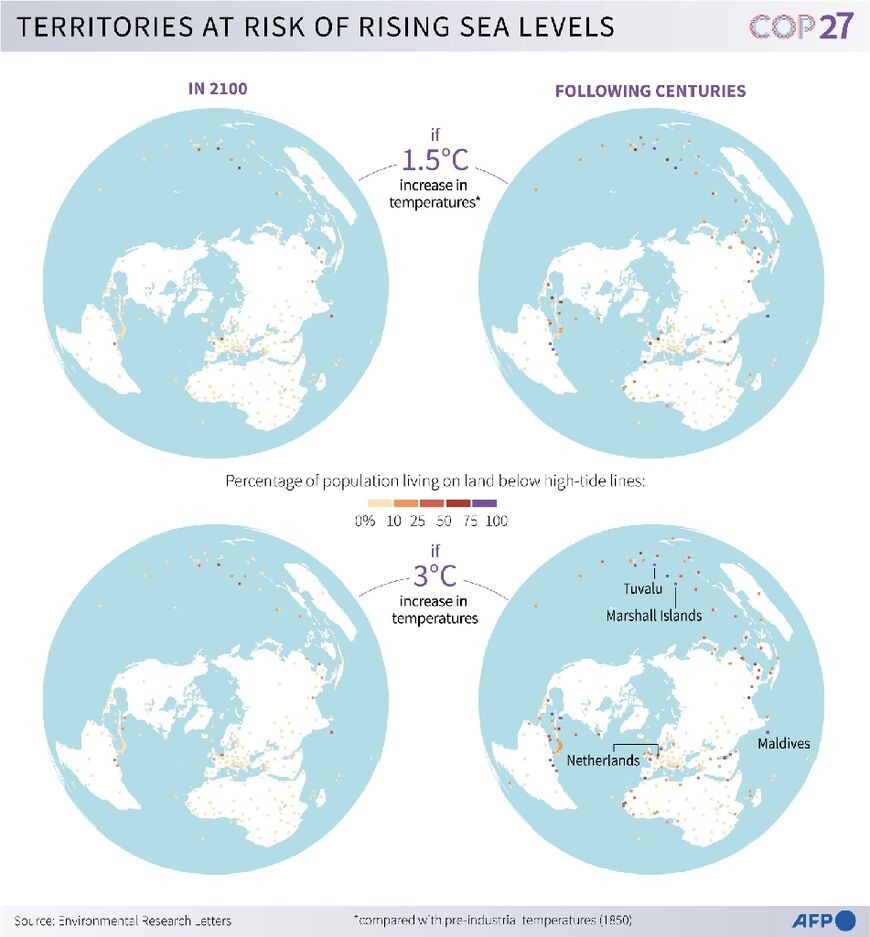
"While they are profiting, the planet is burning," said Browne, who was speaking on behalf of the 39-nation Alliance of Small Island States, many of whose very existence is threatened by rising sea levels and increasingly intense tropical storms.
Barbados Prime Minister Mia Mottley called Monday for a 10 percent tax on oil companies to fund loss and damage.
German Chancellor Olaf Scholz, however, told reporters "here is not the place... to develop fiscal rules."
The contentious question of loss and damage was added to the COP27 agenda after intense negotiations.
The United States and European Union have dragged their feet on the issue in the past, fearful of creating an open-ended reparations regime.
Browne later told reporters that China and India, while not considered developed countries, should also fund loss and damage as they are the world's top and third biggest emitters of greenhouse gases, respectively.
"China and India are major polluters, and the polluter must pay. I don't think there is any free pass for any country," he said.
The goal was to "accelerate" discussion on a loss and damage fund at COP27, he said, with the aim of having a mechanism in place at the next summit and for it to be "truly" operational by 2024.
- 'Can't sink our dreams' -
Another island nation, Tuvalu, announced it was joining calls for a fossil fuel non-proliferation treaty, an initiative that seeks to stop new investments in coal, oil and gas globally and phase out production.
"The warming seas are starting to swallow our lands –- inch by inch," Tuvalu's Prime Minister Kausea Natano said in a statement.
"But the world's addiction to oil, gas and coal can't sink our dreams under the waves," he said.
A Pacific neighbour, Vanuatu, was the first nation to join the treaty in September.
"Vanuatu and Tuvalu are the first countries to call for a new treaty as a companion to the Paris Agreement to align oil, gas and coal production with a global carbon budget," said Tzeporah Berman, chair of the Fossil Fuel Non-Proliferation Treaty initiative.
"We will look back on this in history as the moment of reckoning, with overproduction that is locking in further emissions and holding us back from bending the curve," Berman said.
Browne also recalled that his country and Tuvalu are among four island nations that have had registered a commission with the UN to "explore the responsibility of states for injuries arising from their climate actions and breaches in the obligations".
"As small countries this is a new dynamic pathway of justice where the polluter pays," he said.
Browne said small island states "will fight unrelentingly this climate crisis, and this includes fighting in the international courts and under international law".